1. The Problem
- Costly: Standard RLVR generates thousands of rollouts.
- Inefficient: Many samples are too easy or too hard (zero advantage).
- Goal: Data-efficient RLVR training using data intrinsic properties.
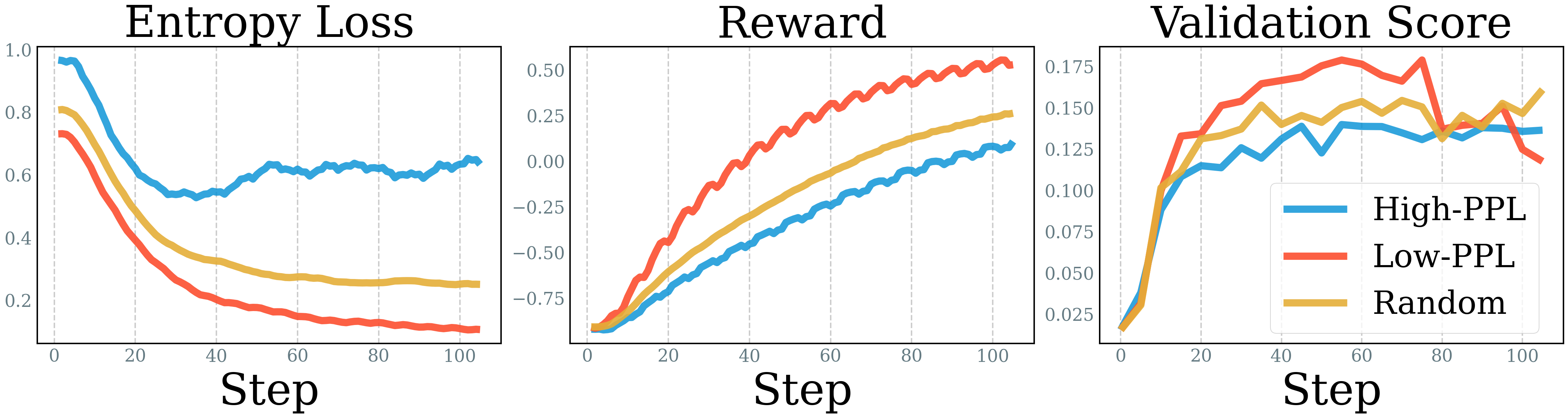
2. Preliminary Analysis
3. Method: Online Prompt Selection
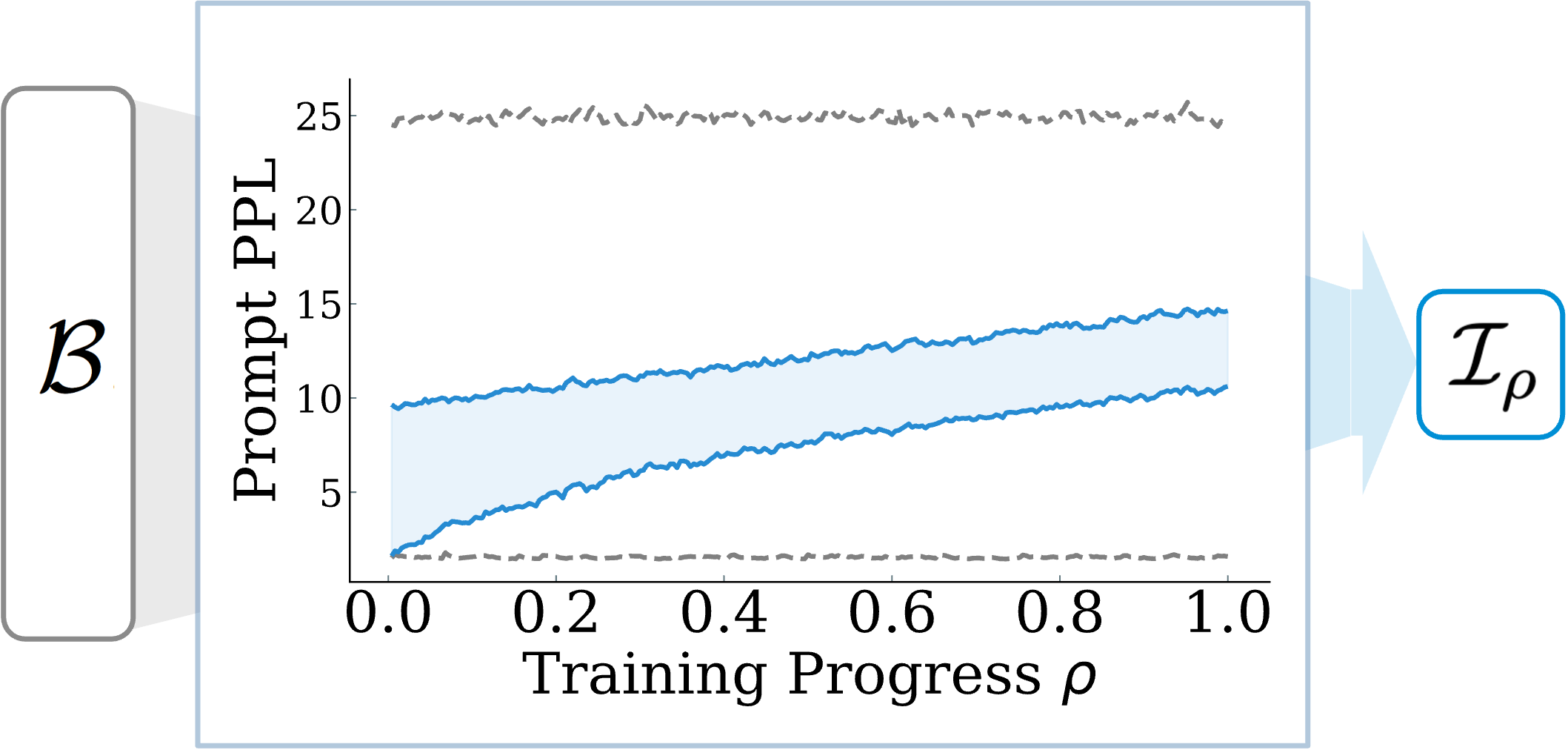
Strategy: Prompt Perplexity
Use perplexity as a proxy to select from a candidate batch $\mathcal{B}$ to the actual batch $\mathcal{I}_{\rho}$ at every training step. Train on Low PPL to High PPL prompts.
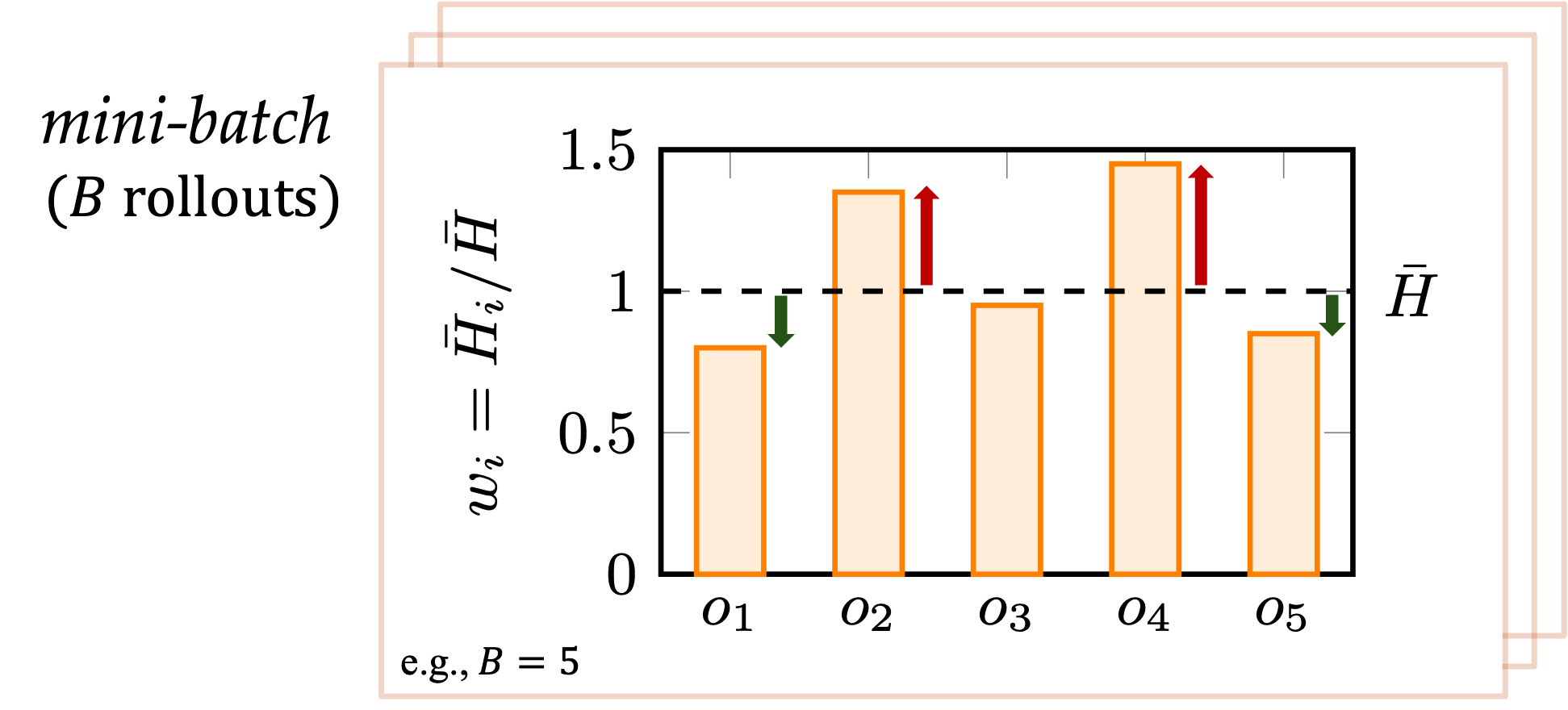
4. Method: Rollout Weighting
Strategy: Relative Entropy
Prioritize diverse reasoning paths. Weight rollouts by their average token-level entropy. ($V$: vocabulary size)
$$\bar{H}_i = -\frac{1}{|o_i|}\sum_{t=1}^{|o_i|} \sum_{v \in V} p(v|x_{t}) \log p(v|x_{t})$$
5. Results
Tested on Qwen & Llama (MATH500, AIME, Olympiad)
| Model | Method | Avg Acc. | Rollouts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen2.5-Math-7B |
Random | 39.45% | 905K |
| PREPO | 39.59% | 540K (1.7x) | |
| Qwen3-4B |
Random | 71.33% | 553K |
| PREPO | 75.99% | 348K (1.6x) |